Polyisoprene a polymer of isoprene c5h8 that is the primary chemical constituent of natural rubber of the naturally occurring resins balata and gutta percha and of the synthetic equivalents of these.
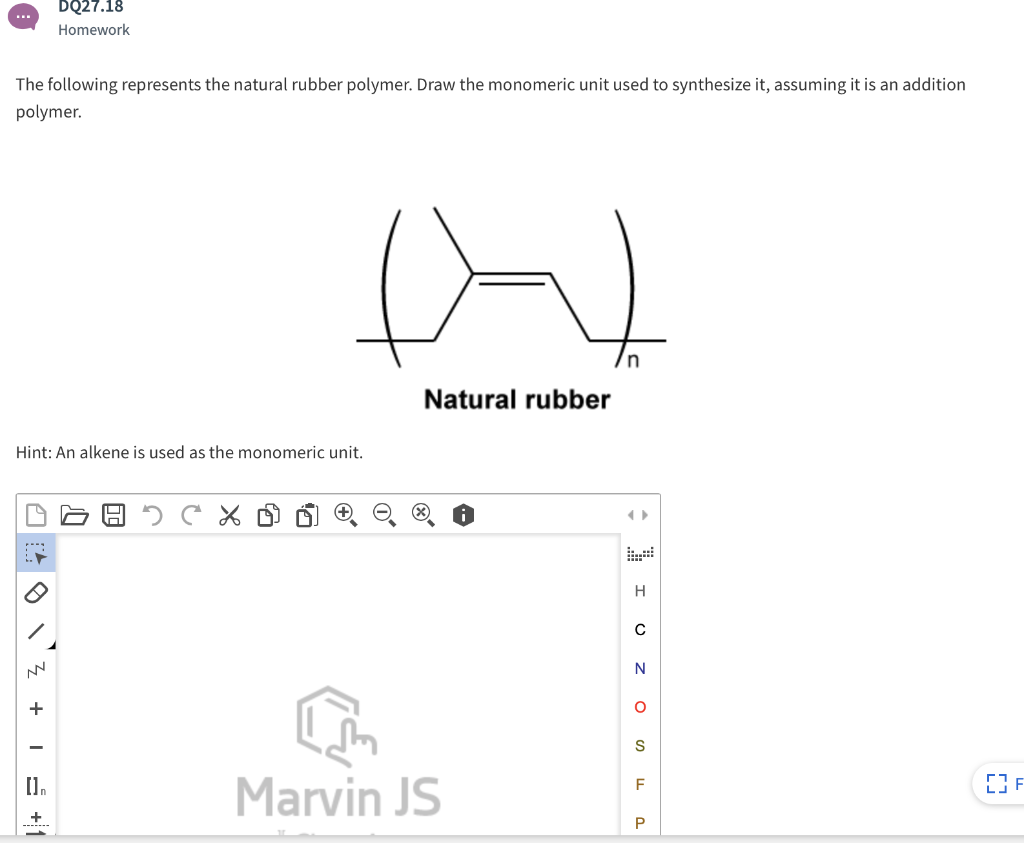
Monomer unit of natural rubber is.
Macro considerations natural rubber is a polymer a long chain like molecule that contains repeating subunits.
It is produced by many plants and animals including humans and its polymers are the main component of natural rubber.
Microstructure refers to the way individual monomer units are distributed along the chain and the geometry in which they are distributed.
The term polymer comes from the greek poly meaning many and mer meaning parts.
The particular monomer units of polymers are produced by the petrochemical processes of distillation of crude oil.
Isoprene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Introduction of natural rubber.
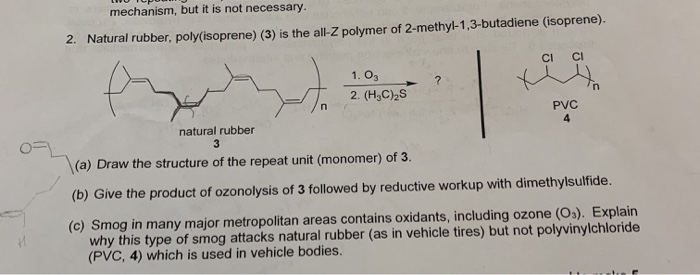
Natural rubber is from the monomer isoprene 2 methyl 1 3 butadiene.
During the distillation of crude oil the hydrocarbon molecular chains are divided into gas benzin diesel and heavy fuel.
Types of polyisoprene that are used as natural rubbers are classified as elastomers.
The monomer of natural rubber is isoprene.
Natural rubber also called india rubber latex amazonian rubber caucho or caoutchouc as initially produced consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene with minor impurities of other organic compounds plus water thailand and indonesia are two of the leading rubber producers.
Natural rubber is unstable to heat.
Natural rubber is insoluble in water.
Isoprene or 2 methyl 1 3 butadiene is a common organic compound with the formula ch 2 c ch 3 ch ch 2 in its pure form it is a colorless volatile liquid.
Natural rubber is an addition polymer that is obtained as a milky white fluid known as the latex from a tropical rubber tree.
A when it is warmed above 50 c it softens and becomes sticky.
A the long hydrocarbon chains of natural rubber cannot dissolve in water.
What is the monomer unit of natural rubber.